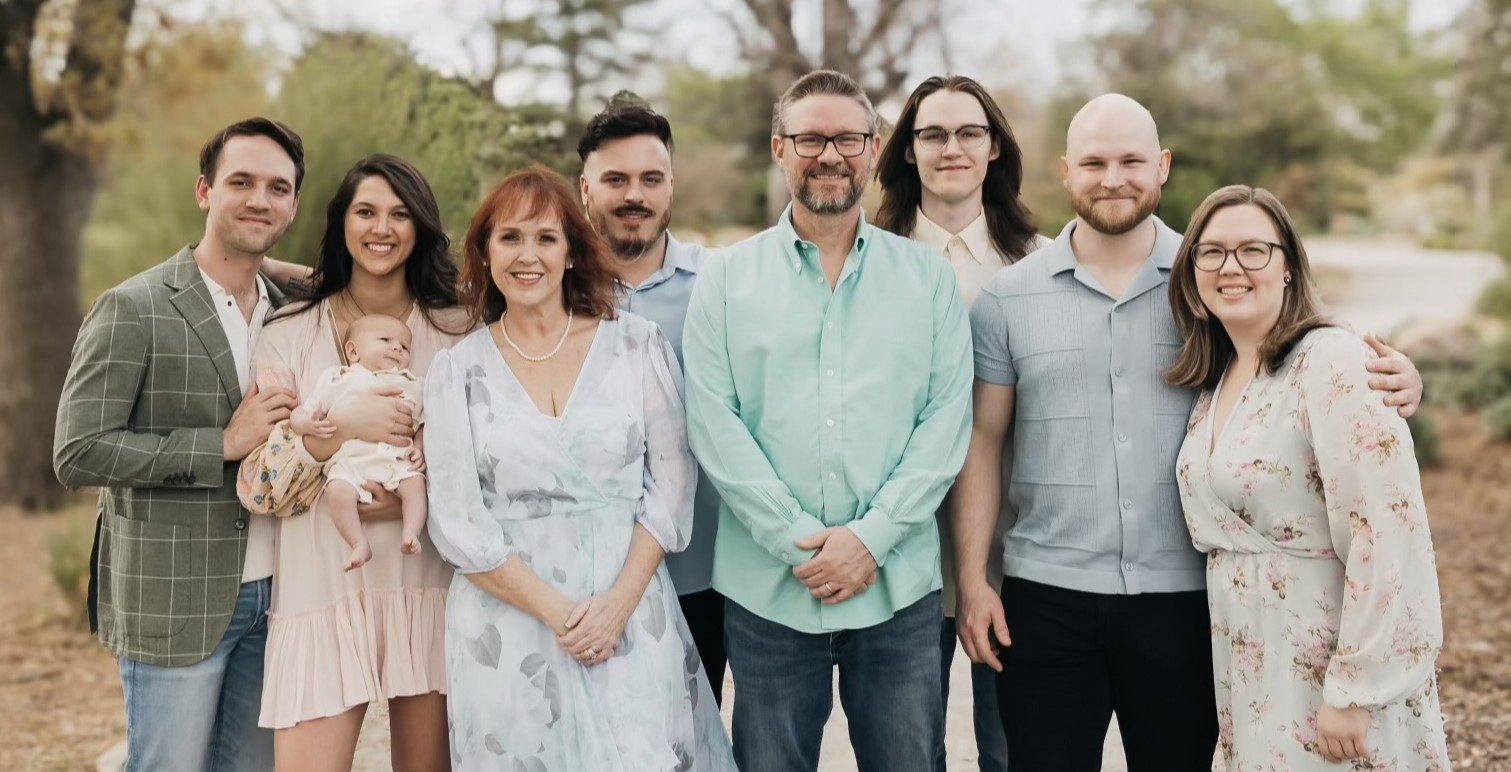
A Conversation with Caryl Ridgeway, Chris Baker, and Cayden Ridgeway
This article is the sixth in a series showcasing parent/child dynamics across the senior housing and care industry. My conversation with the Ridgeway family of Milestone Retirement Companies explores how our industry has become a family affair.
Tell us about your background.
Caryl: I was first introduced to long term care as a 5-year-old when my grandmother would perform at different nursing homes. I was so enamored by the way the residents looked forward to her visits, they just lit up when she sang. One time I asked her “Why do you do this?” and she said: “Because I may be the only happy face they see all day.” I loved being a part of it. I was certain this would be work that I would do someday, even though I didn’t know what exactly that meant at the time. At 15-years-old, I got a job at the same nursing home I would go to with my grandma, all while my friends were working fast food or retail. They didn’t understand but I knew it was fulfilling a need for me and for the residents.
My father was a civil servant and wanted me to pursue his career path out of high school, but I wanted to continue my servant leadership. My senior year of high school, I qualified as a direct hire for the civil servant test, and they offered me a job. I took the position but knew I missed the human connection that I had watched my grandma create. During my civil servant career in accounting, I obtained my EMT certificate and enrolled in nursing school. I was in my final clinical rotation when the Oklahoma City bombing happened, and I ended up assisting with disaster recovery. I missed my entire final rotation for nursing school, so I didn’t graduate. I ultimately chose not to pursue nursing.

In 2005, I had a life-changing event and ended up with a pacemaker. I decided I was going to follow my passion and make it count. I applied to be an Executive Director at a local assisted living facility and fell in love with the position. I worked in every position within the community and found that good culture can make or break a team.
It was during this time that I met the former Milestone owners. With my ‘operator’ brain and my ‘clinical’ thinking skills, I became an asset for their strategy to course-correct some challenging buildings, which I love to do. I then spent two years being CSO, two years being COO, and the last 20 months being CEO. Last year when my partners wanted to retire and sell the company, I approached my husband Scott about purchasing it and continuing the dream of making a difference.
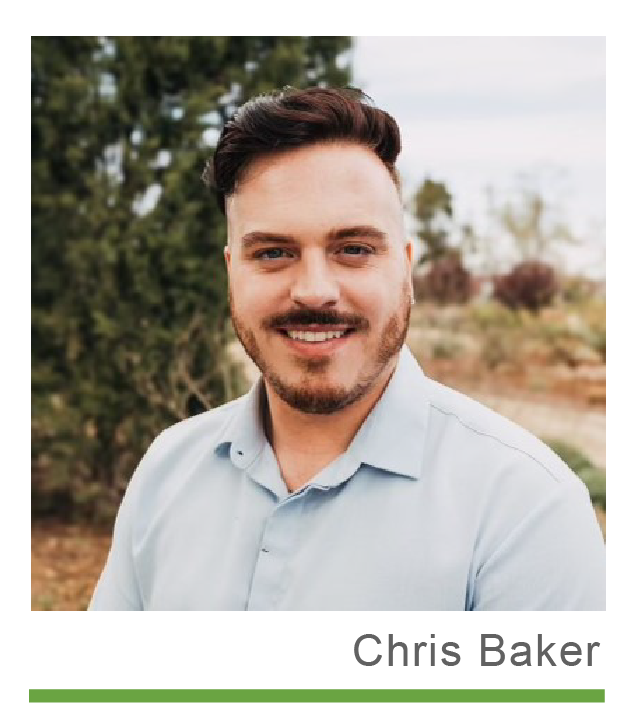

Chris: As I was growing up, I saw how passionate my mom was about her work. At one point, I was a housekeeper for the property where she started. I went to college for music initially, but after I graduated with my associates degree in vocal performance, I decided I didn’t want to be a musician. I had an early interest in death care and got my bachelor’s in funeral sciences—learning how bodies are prepared, how services are conducted, etc. From a healthcare perspective, it showed me the impact you can make on families in need of comfort, guidance, and direction. I apprenticed at a funeral home in Oklahoma City before joining Integris, one of the largest hospital chains in Oklahoma. I stayed with them for four years as an admitting specialist.
In 2018, I was working for a neurology clinic when the doctor closed her practice. I saw it as an opportunity to try something new and so I moved to Austin and joined a logistics company doing risk and compliance. It was different stakes and a different industry, but I learned so much in the four years I was there. My mom had been observing my work and encouraged me to join Milestone as the Director of Risk and Compliance.
Cayden: College wasn’t for me, and I dropped out three times (laughing). I was accepted, and had a scholarship, to go to Berklee College of Music in Boston but decided not to go. I was playing drums for an artist who made it to the end of American Idol but wrestled between a career in music or business. I saw an opening for a position at the Mansion at Waterford, a community my mom oversaw as regional operations. They were looking for someone to build a new program to capture ancillary revenue from private sitters. I applied and when they noticed my last name, I asked them to not tell my mom. If I got it, I wanted it to be on my own merit, not because she was in regional operations. They ended up going with me and I built out the program.
Caryl: We basically eliminated the risk of third-party sitter agencies by bringing the service in-house. It also ended up saving the residents money and under Cayden the program ended up generating a ton of revenue.
Cayden: After that, I worked in sales at a renewable energy startup. I came on as one of the first few sales guys, and over time helped grow their residential sales business. I did so well in it that I eventually moved up to launch and manage their commercial sales division, helping them become the largest solar installation company in the state. During that time, I wanted to own my first home but what I wanted was too expensive to buy, so I built it myself when I was 22. That little experiment went so well that the developers I worked with urged me to start a construction company and so I decided to do that too.

Fast forward to July 2023, my mom had just bought Milestone, and we were having a conversation about it one night. We talked about where they were, the way that it was structured internally, etc., and I made some suggestions that she thought were valuable. Naturally, being the sales guy I am, I then made a pitch deck and presented it to her and the senior leadership team. They liked my vision and the experience I bring from outside the industry, and that presentation is what led to me being offered the Chief Strategy Officer position. My role now is more like that of a Chief Commercial or Chief Growth Officer as I’m in charge of all marketing, sales, business development, investor relations, and strategy. I’ve found that senior living isn’t where it needs to be, which makes me excited, and bullish, about where we can take it.
How do you keep separation between church and state?
Caryl: Whether willingly or not, these boys and their two other siblings grew up in the industry. Being an executive director meant going to the building at 2:00am when the pipes burst and being on calls on weekends and holidays. The kids were so little that I’d drag them with me to everything I did. They got immersed in that multigenerational culture. I probably “talk work” a lot more than I’m aware of, but since they’ve joined, I’ve been very intentional about cutting back and focusing on family when we’re together.
Chris: I live in a different state, so I get a little dopamine rush when I see my family members’ names pop up over email. Working with them has allowed me more opportunities to connect, which is excellent because I don’t see them every day.
Whenever my mom and I hop on a call, it doesn’t feel like work because we’re on the same page. It’s not laborious. We don’t ever butt heads and she’s an excellent sounding board. I tell people that it’s a surreal, once in a lifetime opportunity to come aboard and help navigate the family company ship. I’m grateful for the balance we’ve created.
Cayden: For me, the reality is that we “talk work” a ton and it’s interwoven into almost everything we do. I didn’t grow up with my mom owning the company, I grew up watching her grind it out and drive generators to her properties. I’ve been so proud watching her ascend into this position because I’ve been witness to many of the sacrifices she’s made to get here. It’s not all easy though—Mom and I definitely butt heads—but I enjoy that. We challenge each other and, in the end, we always arrive at a place that’s best for the company.
What advice do you have for your sons and the next generation?
Caryl: We are a relationship-based industry, and as long as we’re humans caring for humans, that isn’t going to change. The minute you get out of touch with what’s going on in your buildings, you risk losing that relationship component.
I insist on being knowledgeable about what’s going on at the community level. If I’m a desk CEO then I’m no good to the field. My advice is to not lose touch with the relationships that are on the front line driving your business. You can have all the tech in the world, but it won’t matter when you can’t answer questions about a resident when their family calls.

What advice do you have for the previous generation?
Cayden: Man, what a loaded question! I think that for the industry to make groundbreaking change, there will have to be people willing to break outside this senior living box. So many industry conferences are based on accelerating change and while it’s a nice feeling, I don’t see it happening fast enough yet. We need to pull from other industries and apply those to senior living, but it doesn’t work if only a handful of us are doing it. In my opinion, leaning into change (or leading the change) coupled with your ability to adapt to increasingly competitive conditions, will be the make or break for many over the next five years.
Chris: My advice is to always navigate the space with the people who you’re serving in mind. Risk can be viewed in a very non-human way, but I remind myself that I serve our residents and the people who work for us. The biggest distinguishing factor from working at a great company to working at a not-so-great place, is how people are treated.
Is there anything you want to add?
Caryl: I want to take a moment to shout out the people not on the call. My daughter-in-law Shelby has been my assistant for many years before the boys joined the company. I wanted to give her honorable mention for the time she’s spent putting up with me.
Chris: Shelby is a key player to our success for sure.
Cayden: And then there’s our dad Scott, who serves as Milestone’s Chief Technology Officer. From working for Cerner to his time at EPIC, he’s become a wizard when it comes to medical technology systems.
Caryl: There are so many others who are basically like family, too. I have people working for Milestone today who have worked with me for more than 20 years.
Cayden: The number of people in our family and outside our family that want to follow my mom is a testament to how great of a mother and leader she is.
Caryl: Thanks Cayden, you just got a better Christmas present!